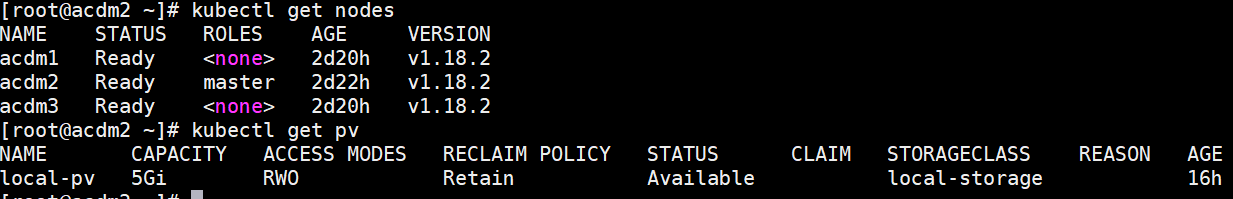
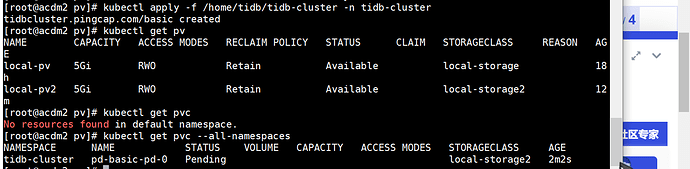
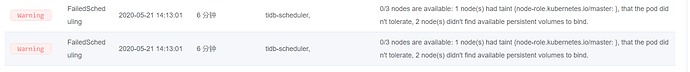
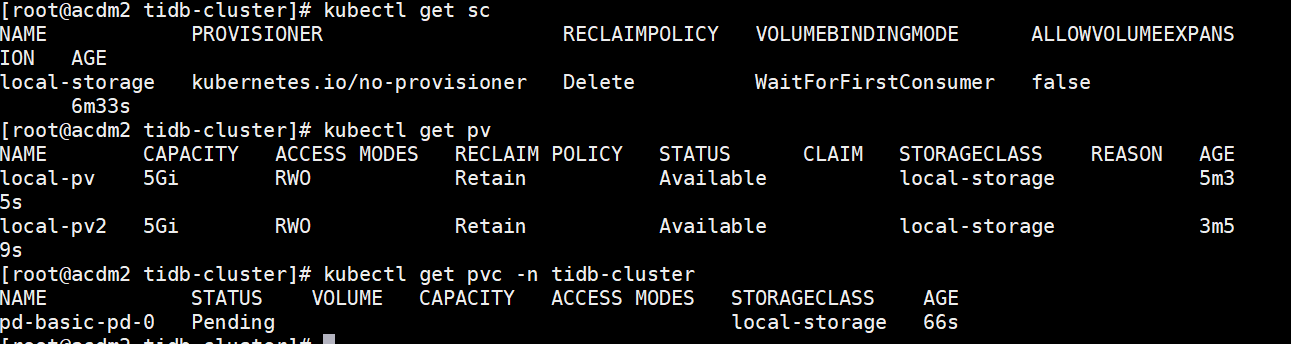
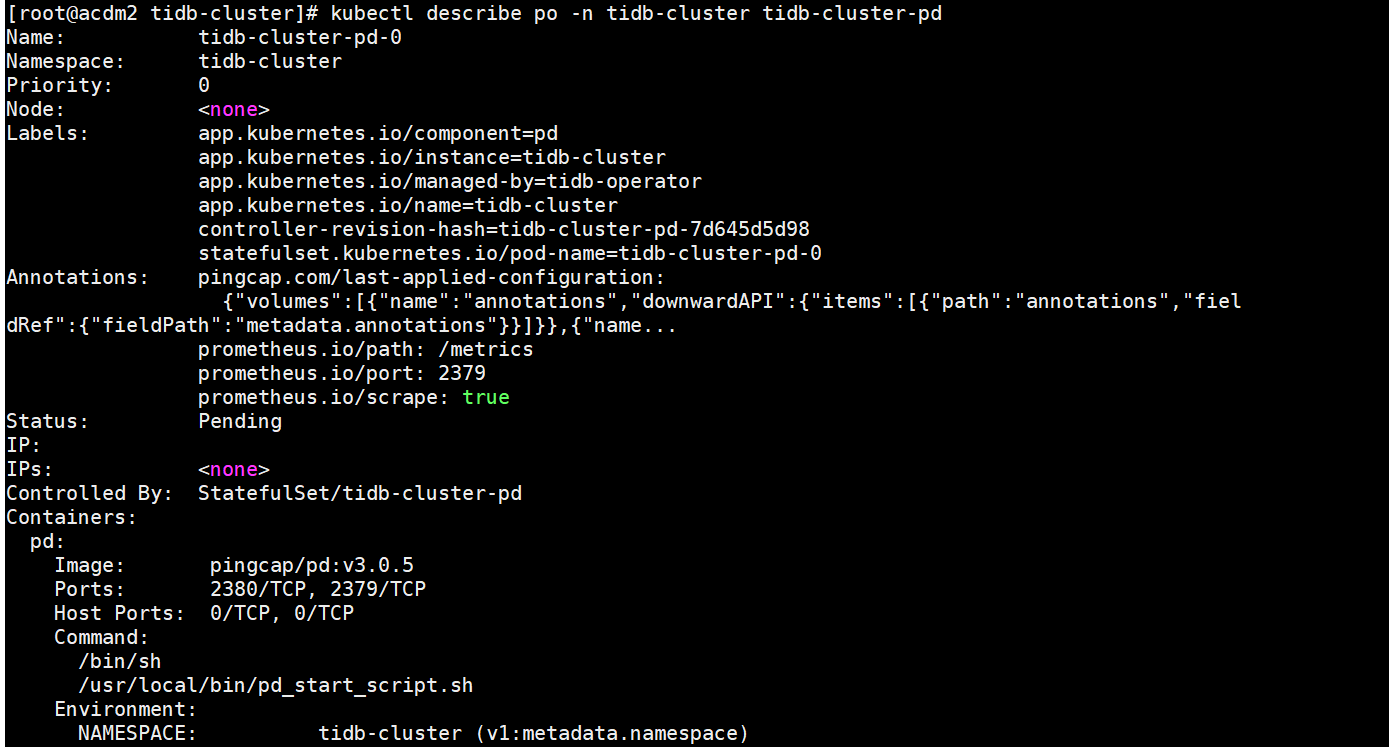
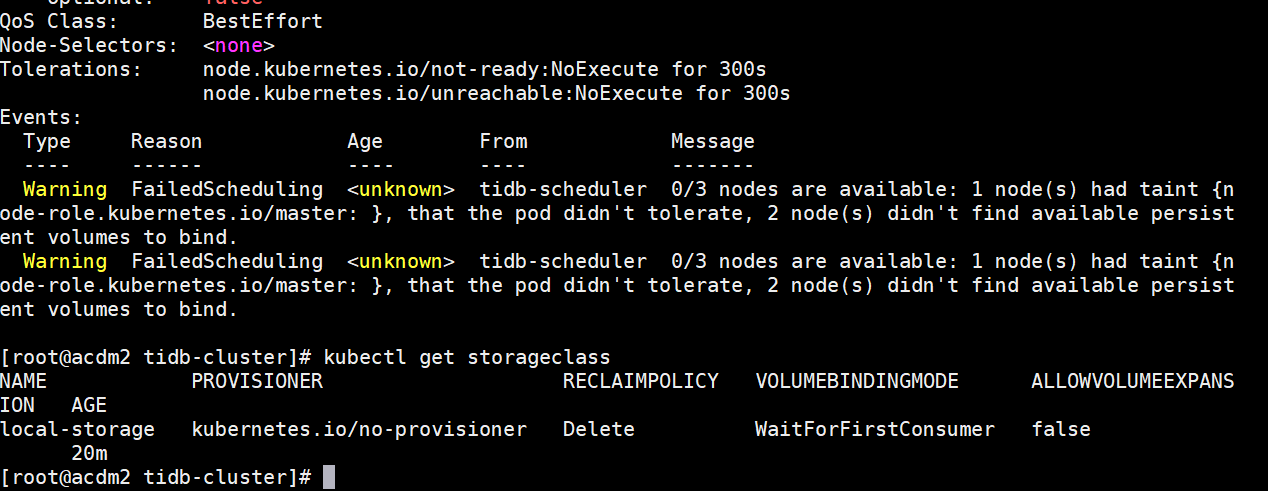
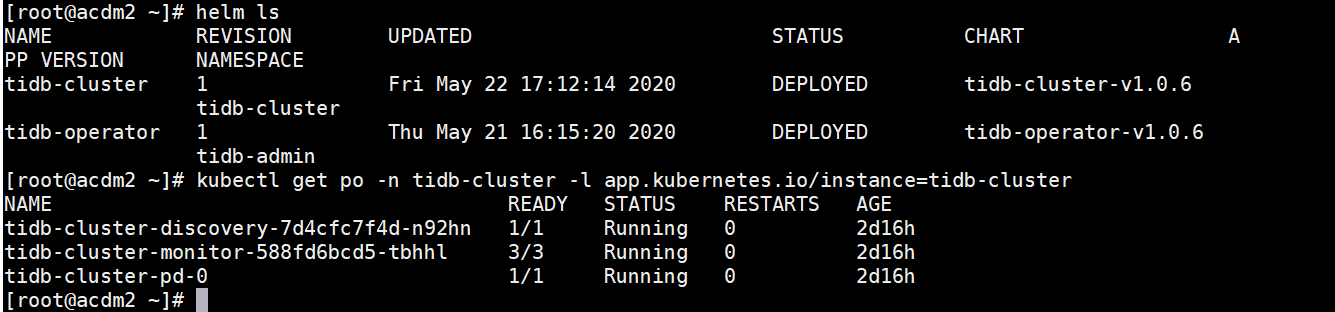
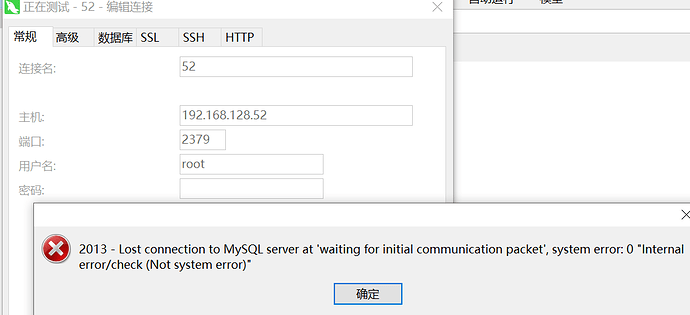
emm 原以为好了,周一来看发现不太行。。。是哪里出问题了么?
连接不上数据库:
我的部署tidb-cluster.yaml如下:
# Default values for tidb-cluster.
# This is a YAML-formatted file.
# Declare variables to be passed into your templates.
# Also see monitor.serviceAccount
# If you set rbac.create to false, you need to provide a value for monitor.serviceAccount
rbac:
create: true
# clusterName is the TiDB cluster name, if not specified, the chart release name will be used
# clusterName: demo
# Add extra labels to TidbCluster object
# ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/overview/working-with-objects/labels/
extraLabels: {}
# schedulerName must be same with charts/tidb-operator/values#scheduler.schedulerName
schedulerName: tidb-scheduler
# timezone is the default system timzone for TiDB
timezone: UTC
# reclaim policy of a PV, default: Retain.
# you must set it to Retain to ensure data safety in production environment.
# https://pingcap.com/docs/v3.0/tidb-in-kubernetes/reference/configuration/local-pv/#data-security
pvReclaimPolicy: Retain
# services is the service list to expose, default is ClusterIP
# can be ClusterIP | NodePort | LoadBalancer
services:
- name: pd
type: ClusterIP
discovery:
image: pingcap/tidb-operator:v1.0.6
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
resources:
limits:
cpu: 250m
memory: 150Mi
requests:
cpu: 80m
memory: 50Mi
# Whether enable ConfigMap Rollout management.
# When enabling, change of ConfigMap will trigger a graceful rolling-update of the component.
# This feature is only available in tidb-operator v1.0 or higher.
# Note: Switch this variable against an existing cluster will cause an rolling-update of each component even
# if the ConfigMap was not changed.
enableConfigMapRollout: true
pd:
# Please refer to https://github.com/pingcap/pd/blob/master/conf/config.toml for the default
# pd configurations (change to the tags of your pd version),
# just follow the format in the file and configure in the 'config' section
# as below if you want to customize any configuration.
# Please refer to https://pingcap.com/docs-cn/v3.0/reference/configuration/pd-server/configuration-file/
# (choose the version matching your pd) for detailed explanation of each parameter.
config: |
[log]
level = "info"
[replication]
location-labels = ["region", "zone", "rack", "host"]
replicas: 1
image: pingcap/pd:v3.0.5
# storageClassName is a StorageClass provides a way for administrators to describe the "classes" of storage they offer.
# different classes might map to quality-of-service levels, or to backup policies,
# or to arbitrary policies determined by the cluster administrators.
# refer to https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/storage/storage-classes
storageClassName: nfs
# Image pull policy.
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
resources:
limits: {}
# cpu: 8000m
# memory: 8Gi
requests:
# cpu: 4000m
# memory: 4Gi
storage: 1Gi
## affinity defines pd scheduling rules,it's default settings is empty.
## please read the affinity document before set your scheduling rule:
## ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/assign-pod-node/#affinity-and-anti-affinity
affinity: {}
## The following is typical example of affinity settings:
## The PodAntiAffinity setting of the example keeps PD pods does not co-locate on a topology node as far as possible to improve the disaster tolerance of PD on Kubernetes.
## The NodeAffinity setting of the example ensure that the PD pods can only be scheduled to nodes with label:[type="pd"],
# affinity:
# podAntiAffinity:
# preferredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
# # this term work when the nodes have the label named region
# - weight: 10
# podAffinityTerm:
# labelSelector:
# matchLabels:
# app.kubernetes.io/instance: <release name>
# app.kubernetes.io/component: "pd"
# topologyKey: "region"
# namespaces:
# - <helm namespace>
# # this term work when the nodes have the label named zone
# - weight: 20
# podAffinityTerm:
# labelSelector:
# matchLabels:
# app.kubernetes.io/instance: <release name>
# app.kubernetes.io/component: "pd"
# topologyKey: "zone"
# namespaces:
# - <helm namespace>
# # this term work when the nodes have the label named rack
# - weight: 40
# podAffinityTerm:
# labelSelector:
# matchLabels:
# app.kubernetes.io/instance: <release name>
# app.kubernetes.io/component: "pd"
# topologyKey: "rack"
# namespaces:
# - <helm namespace>
# # this term work when the nodes have the label named kubernetes.io/hostname
# - weight: 80
# podAffinityTerm:
# labelSelector:
# matchLabels:
# app.kubernetes.io/instance: <release name>
# app.kubernetes.io/component: "pd"
# topologyKey: "kubernetes.io/hostname"
# namespaces:
# - <helm namespace>
# nodeAffinity:
# requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
# nodeSelectorTerms:
# - matchExpressions:
# - key: "kind"
# operator: In
# values:
# - "pd"
## nodeSelector ensure pods only assigning to nodes which have each of the indicated key-value pairs as labels
## ref:https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/assign-pod-node/#nodeselector
nodeSelector: {}
## Tolerations are applied to pods, and allow pods to schedule onto nodes with matching taints.
## refer to https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/taint-and-toleration
tolerations: []
# - key: node-role
# operator: Equal
# value: tidb
# effect: "NoSchedule"
annotations: {}
# Specify the security context of PD Pod.
# refer to https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/configure-pod-container/security-context/#set-the-security-context-for-a-pod
podSecurityContext: {}
# Use the host's network namespace if enabled.
# Default to false.
hostNetwork: false
tikv:
# Please refer to https://github.com/tikv/tikv/blob/master/etc/config-template.toml for the default
# tikv configurations (change to the tags of your tikv version),
# just follow the format in the file and configure in the 'config' section
# as below if you want to customize any configuration.
# Please refer to https://pingcap.com/docs-cn/v3.0/reference/configuration/tikv-server/configuration-file/
# (choose the version matching your tikv) for detailed explanation of each parameter.
config: |
log-level = "info"
# # Here are some parameters you MUST customize (Please configure in the above `tikv.config` section):
#
# [readpool.coprocessor]
# # Normally these three parameters should be tuned to 80% of `tikv.resources.limits.cpu`, for example: 10000m -> 8
# high-concurrency = 8
# normal-concurrency = 8
# low-concurrency = 8
#
# # For TiKV v2.x:
# [rocksdb.defaultcf]
# ## block-cache used to cache uncompressed blocks, big block-cache can speed up read.
# ## in normal cases should tune to 30%-50% `tikv.resources.limits.memory`
# # block-cache-size = "1GB"
#
# [rocksdb.writecf]
# ## in normal cases should tune to 10%-30% `tikv.resources.limits.memory`
# # block-cache-size = "256MB"
#
# # From TiKV v3.0.0 on, you do not need to configure
# # [rocksdb.defaultcf].block-cache-size and [rocksdb.writecf].block-cache-size.
# # Instead, configure [storage.block-cache] as below:
# [storage.block-cache]
# shared = true
#
# # Normally it should be tuned to 30%-50% of `tikv.resources.limits.memory`, for example: 32Gi -> 16GB
# capacity = "1GB"
replicas: 1
image: pingcap/tikv:v3.0.5
# storageClassName is a StorageClass provides a way for administrators to describe the "classes" of storage they offer.
# different classes might map to quality-of-service levels, or to backup policies,
# or to arbitrary policies determined by the cluster administrators.
# refer to https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/storage/storage-classes
storageClassName: nfs
# Image pull policy.
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
resources:
limits: {}
# cpu: 16000m
# memory: 32Gi
# storage: 300Gi
requests:
# cpu: 12000m
# memory: 24Gi
storage: 10Gi
## affinity defines tikv scheduling rules,affinity default settings is empty.
## please read the affinity document before set your scheduling rule:
## ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/assign-pod-node/#affinity-and-anti-affinity
affinity: {}
## nodeSelector ensure pods only assigning to nodes which have each of the indicated key-value pairs as labels
## ref:https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/assign-pod-node/#nodeselector
nodeSelector: {}
## Tolerations are applied to pods, and allow pods to schedule onto nodes with matching taints.
## refer to https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/taint-and-toleration
tolerations: []
# - key: node-role
# operator: Equal
# value: tidb
# effect: "NoSchedule"
annotations: {}
# When a TiKV node fails, its status turns to `Disconnected`. After 30 minutes, it turns to `Down`.
# After waiting for 5 minutes, TiDB Operator creates a new TiKV node if this TiKV node is still down.
# maxFailoverCount is used to configure the maximum number of TiKV nodes that TiDB Operator can create when failover occurs.
maxFailoverCount: 3
# Specify the security context of TiKV Pod.
# refer to https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/configure-pod-container/security-context/#set-the-security-context-for-a-pod
podSecurityContext: {}
# Use the host's network namespace if enabled.
# Default to false.
hostNetwork: false
tidb:
# Please refer to https://github.com/pingcap/tidb/blob/master/config/config.toml.example for the default
# tidb configurations(change to the tags of your tidb version),
# just follow the format in the file and configure in the 'config' section
# as below if you want to customize any configuration.
# Please refer to https://pingcap.com/docs-cn/v3.0/reference/configuration/tidb-server/configuration-file/
# (choose the version matching your tidb) for detailed explanation of each parameter.
config: |
[log]
level = "info"
# # Here are some parameters you MUST customize (Please configure in the above 'tidb.config' section):
# [performance]
# # Normally it should be tuned to `tidb.resources.limits.cpu`, for example: 16000m -> 16
# max-procs = 0
replicas: 2
# The secret name of root password, you can create secret with following command:
# kubectl create secret generic tidb-secret --from-literal=root=<root-password> --namespace=<namespace>
# If unset, the root password will be empty and you can set it after connecting
# passwordSecretName: tidb-secret
# permitHost is the host which will only be allowed to connect to the TiDB.
# If unset, defaults to '%' which means allow any host to connect to the TiDB.
# permitHost: 127.0.0.1
# initSql is the SQL statements executed after the TiDB cluster is bootstrapped.
# initSql: |-
# create database app;
image: pingcap/tidb:v3.0.5
# Image pull policy.
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
resources:
limits: {}
# cpu: 16000m
# memory: 16Gi
requests: {}
# cpu: 12000m
# memory: 12Gi
## affinity defines tikv scheduling rules,affinity default settings is empty.
## please read the affinity document before set your scheduling rule:
## ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/assign-pod-node/#affinity-and-anti-affinity
affinity: {}
## If binlog.pump is enabled, the following affinity is recommended to make tidb and pump deploy at the same node in production
## to avoid losing binlog in tidb if there was network partition error.
# podAffinity:
# requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
# - labelSelector:
# matchExpressions:
# - key: "app.kubernetes.io/component"
# operator: In
# values:
# - "pump"
# - key: "app.kubernetes.io/managed-by"
# operator: In
# values:
# - "tidb-operator"
# - key: "app.kubernetes.io/name"
# operator: In
# values:
# - "tidb-cluster"
# - key: "app.kubernetes.io/instance"
# operator: In
# values:
# - <release-name>
# topologyKey: kubernetes.io/hostname
## nodeSelector ensure pods only assigning to nodes which have each of the indicated key-value pairs as labels
## ref:https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/assign-pod-node/#nodeselector
nodeSelector: {}
## Tolerations are applied to pods, and allow pods to schedule onto nodes with matching taints.
## refer to https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/taint-and-toleration
tolerations: []
# - key: node-role
# operator: Equal
# value: tidb
# effect: "NoSchedule"
annotations: {}
# Specify the security context of TiDB Pod.
# refer to https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/configure-pod-container/security-context/#set-the-security-context-for-a-pod
podSecurityContext: {}
# Use the host's network namespace if enabled.
# Default to false.
hostNetwork: false
maxFailoverCount: 3
service:
type: NodePort
exposeStatus: true
# annotations:
# cloud.google.com/load-balancer-type: Internal
separateSlowLog: true
slowLogTailer:
image: busybox:1.26.2
resources:
limits:
cpu: 100m
memory: 50Mi
requests:
cpu: 20m
memory: 5Mi
initializer:
resources: {}
# limits:
# cpu: 100m
# memory: 100Mi
# requests:
# cpu: 100m
# memory: 100Mi
# tidb plugin configuration
plugin:
# enable plugin or not
enable: false
# the start argument to specify the folder containing
directory: /plugins
# the start argument to specify the plugin id (name "-" version) that needs to be loaded, e.g. 'conn_limit-1'.
list: ["whitelist-1"]
# mysqlClient is used to set password for TiDB
# it must has Python MySQL client installed
mysqlClient:
image: tnir/mysqlclient
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
monitor:
create: true
# Also see rbac.create
# If you set rbac.create to false, you need to provide a value here.
# If you set rbac.create to true, you should leave this empty.
# serviceAccount:
persistent: false
storageClassName: nfs
storage: 10Gi
initializer:
image: pingcap/tidb-monitor-initializer:v3.0.5
imagePullPolicy: Always
config:
K8S_PROMETHEUS_URL: http://prometheus-k8s.monitoring.svc:9090
resources: {}
# limits:
# cpu: 50m
# memory: 64Mi
# requests:
# cpu: 50m
# memory: 64Mi
reloader:
create: true
image: pingcap/tidb-monitor-reloader:v1.0.1
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
service:
type: NodePort
resources:
# limits:
# cpu: 50m
# memory: 64Mi
# requests:
# cpu: 50m
# memory: 64Mi
grafana:
create: true
image: grafana/grafana:6.0.1
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
logLevel: info
resources:
limits: {}
# cpu: 8000m
# memory: 8Gi
requests: {}
# cpu: 4000m
# memory: 4Gi
username: admin
password: admin
config:
# Configure Grafana using environment variables except GF_PATHS_DATA, GF_SECURITY_ADMIN_USER and GF_SECURITY_ADMIN_PASSWORD
# Ref https://grafana.com/docs/installation/configuration/#using-environment-variables
GF_AUTH_ANONYMOUS_ENABLED: "true"
GF_AUTH_ANONYMOUS_ORG_NAME: "Main Org."
GF_AUTH_ANONYMOUS_ORG_ROLE: "Viewer"
# if grafana is running behind a reverse proxy with subpath http://foo.bar/grafana
# GF_SERVER_DOMAIN: foo.bar
# GF_SERVER_ROOT_URL: "%(protocol)s://%(domain)s/grafana/"
service:
type: NodePort
prometheus:
image: prom/prometheus:v2.11.1
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
logLevel: info
resources:
limits: {}
# cpu: 8000m
# memory: 8Gi
requests: {}
# cpu: 4000m
# memory: 4Gi
service:
type: NodePort
reserveDays: 12
# alertmanagerURL: ""
nodeSelector: {}
# kind: monitor
# zone: cn-bj1-01,cn-bj1-02
# region: cn-bj1
tolerations: []
# - key: node-role
# operator: Equal
# value: tidb
# effect: "NoSchedule"
binlog:
pump:
create: false
replicas: 1
image: pingcap/tidb-binlog:v3.0.5
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
logLevel: info
# storageClassName is a StorageClass provides a way for administrators to describe the "classes" of storage they offer.
# different classes might map to quality-of-service levels, or to backup policies,
# or to arbitrary policies determined by the cluster administrators.
# refer to https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/storage/storage-classes
storageClassName: nfs
storage: 20Gi
# affinity for pump pod assignment, default: empty
# ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/assign-pod-node/#affinity-and-anti-affinity
affinity: {}
## The following setting is recommended to make each pump instance be distributed deployed in each node
## Each node is recommended at most have one pump instance deployed.
# podAntiAffinity:
# preferredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
# - weight: 100
# podAffinityTerm:
# labelSelector:
# matchExpressions:
# - key: "app.kubernetes.io/component"
# operator: In
# values:
# - "pump"
# - key: "app.kubernetes.io/managed-by"
# operator: In
# values:
# - "tidb-operator"
# - key: "app.kubernetes.io/name"
# operator: In
# values:
# - "tidb-cluster"
# - key: "app.kubernetes.io/instance"
# operator: In
# values:
# - <release-name>
# topologyKey: kubernetes.io/hostname
# tolerations are applied to pods, and allow pods to schedule onto nodes with matching taints.
# refer to https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/taint-and-toleration
tolerations: []
syncLog: true
# a integer value to control expiry date of the binlog data, indicates for how long (in days) the binlog data would be stored.
# must bigger than 0
gc: 7
# number of seconds between heartbeat ticks (in 2 seconds)
heartbeatInterval: 2
resources:
limits: {}
# cpu: 8000m
# memory: 8Gi
requests: {}
# cpu: 4000m
# memory: 4Gi
# Please refer to https://github.com/pingcap/tidb-binlog/blob/master/cmd/pump/pump.toml for the default
# pump configurations (change to the tags of your pump version),
# just follow the format in the file and configure in the 'config' section
# as below if you want to customize any configuration.
# config: |
# gc = 7
# heartbeat-interval = 2
# [storage]
# sync-log = true
# stop-write-at-available-space = "10Gi"
drainer:
create: false
image: pingcap/tidb-binlog:v3.0.5
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
logLevel: info
# storageClassName is a StorageClass provides a way for administrators to describe the "classes" of storage they offer.
# different classes might map to quality-of-service levels, or to backup policies,
# or to arbitrary policies determined by the cluster administrators.
# refer to https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/storage/storage-classes
storageClassName: nfs
storage: 10Gi
# affinity for drainer pod assignment, default: empty
# ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/assign-pod-node/#affinity-and-anti-affinity
affinity: {}
# tolerations are applied to pods, and allow pods to schedule onto nodes with matching taints.
# refer to https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/taint-and-toleration
tolerations: []
# the number of the concurrency of the downstream for synchronization. The bigger the value,
# the better throughput performance of the concurrency (16 by default)
workerCount: 16
# the interval time (in seconds) of detect pumps' status (default 10)
detectInterval: 10
# disbale detect causality
disableDetect: false
# disable dispatching sqls that in one same binlog; if set true, work-count and txn-batch would be useless
disableDispatch: false
# # disable sync these schema
ignoreSchemas: "INFORMATION_SCHEMA,PERFORMANCE_SCHEMA,mysql,test"
# if drainer donesn't have checkpoint, use initial commitTS to initial checkpoint
initialCommitTs: 0
# enable safe mode to make syncer reentrant
safeMode: false
# the number of SQL statements of a transaction that are output to the downstream database (20 by default)
txnBatch: 20
# downstream storage, equal to --dest-db-type
# valid values are "mysql", "pb", "kafka"
destDBType: pb
mysql: {}
# host: "127.0.0.1"
# user: "root"
# password: ""
# port: 3306
# # Time and size limits for flash batch write
# timeLimit: "30s"
# sizeLimit: "100000"
kafka: {}
# only need config one of zookeeper-addrs and kafka-addrs, will get kafka address if zookeeper-addrs is configed.
# zookeeperAddrs: "127.0.0.1:2181"
# kafkaAddrs: "127.0.0.1:9092"
# kafkaVersion: "0.8.2.0"
resources:
limits: {}
# cpu: 8000m
# memory: 8Gi
requests: {}
# cpu: 4000m
# memory: 4Gi
# Please refer to https://github.com/pingcap/tidb-binlog/blob/master/cmd/drainer/drainer.toml for the default
# drainer configurations (change to the tags of your drainer version),
# just follow the format in the file and configure in the 'config' section
# as below if you want to customize any configuration.
# config: |
# detect-interval = 10
# [syncer]
# worker-count = 16
# disable-dispatch = false
# ignore-schemas = "INFORMATION_SCHEMA,PERFORMANCE_SCHEMA,mysql"
# safe-mode = false
# txn-batch = 20
# db-type = "mysql"
# [syncer.to]
# # host = "127.0.0.1"
# # user = "root"
# # password = ""
# # port = 3306
scheduledBackup:
create: false
# https://github.com/pingcap/tidb-cloud-backup
mydumperImage: pingcap/tidb-cloud-backup:20190828
mydumperImagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
# storageClassName is a StorageClass provides a way for administrators to describe the "classes" of storage they offer.
# different classes might map to quality-of-service levels, or to backup policies,
# or to arbitrary policies determined by the cluster administrators.
# refer to https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/storage/storage-classes
storageClassName: nfs
storage: 100Gi
# https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/job/automated-tasks-with-cron-jobs/#schedule
schedule: "0 0 * * *"
# https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/job/automated-tasks-with-cron-jobs/#suspend
suspend: false
# https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/job/automated-tasks-with-cron-jobs/#jobs-history-limits
successfulJobsHistoryLimit: 3
failedJobsHistoryLimit: 1
# https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/job/automated-tasks-with-cron-jobs/#starting-deadline
startingDeadlineSeconds: 3600
# -t is thread count, larger thread count will speed up the backup, but may impact the performance of the upstream TiDB.
# -F is the chunk size, a big table is partitioned into many chunks.
# Other useful options are -B for database, and -T for tables.
# See https://github.com/maxbube/mydumper/blob/master/docs/mydumper_usage.rst#options for more options.
options: "-t 16 -F 256 --skip-tz-utc --verbose=3"
# The time limit during which data is retained for each GC when backup, in the format of Go Duration.
# When a GC happens, the current time minus this value is the safe point.
tikvGCLifeTime: 720h
# secretName is the name of the secret which stores user and password used for backup
# Note: you must give the user enough privilege to do the backup
# you can create the secret by:
# kubectl create secret generic backup-secret --from-literal=user=root --from-literal=password=<password>
secretName: backup-secret
# backup to gcp
gcp: {}
# bucket: ""
# secretName is the name of the secret which stores the gcp service account credentials json file
# The service account must have read/write permission to the above bucket.
# Read the following document to create the service account and download the credentials file as credentials.json:
# https://cloud.google.com/docs/authentication/production#obtaining_and_providing_service_account_credentials_manually
# And then create the secret by: kubectl create secret generic gcp-backup-secret --from-file=./credentials.json
# secretName: gcp-backup-secret
# backup to ceph object storage
ceph: {}
# endpoint: ""
# bucket: ""
# secretName is the name of the secret which stores ceph object store access key and secret key
# You can create the secret by:
# kubectl create secret generic ceph-backup-secret --from-literal=access_key=<access-key> --from-literal=secret_key=<secret-key>
# secretName: ceph-backup-secret
# backup to s3
s3: {}
# region: ""
# bucket: ""
# secretName is the name of the secret which stores s3 object store access key and secret key
# You can create the secret by:
# kubectl create secret generic s3-backup-secret --from-literal=access_key=<access-key> --from-literal=secret_key=<secret-key>
# secretName: s3-backup-secret
resources:
limits: {}
# cpu: 8000m
# memory: 8Gi
requests: {}
# cpu: 4000m
# memory: 4Gi
importer:
create: false
image: pingcap/tidb-lightning:v3.0.1
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
storageClassName: nfs
storage: 200Gi
resources: {}
# limits:
# cpu: 16000m
# memory: 8Gi
# requests:
# cpu: 16000m
# memory: 8Gi
affinity: {}
tolerations: []
pushgatewayImage: prom/pushgateway:v0.3.1
pushgatewayImagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
config: |
log-level = "info"
[metric]
job = "tikv-importer"
interval = "15s"
address = "localhost:9091"
metaInstance: "{{ $labels.instance }}"
metaType: "{{ $labels.type }}"
metaValue: "{{ $value }}"