课程名称: 1.3 A Brief History About the TiDB database platform(TiDB 发展简史)
学习时长:
1 小时
课程收获:
了解TiDB 发展简史
课程内容:
Befor we begin
- Goal: Introduce a brief history of TiDB
- Outline:
- Ancient days of TiDB
- TiDB with TiSpark
- TiDB with TiFlash
Ancient days of TiDB
- Inspired by Google Spanner,we made TiDB
- In the 1.0.0 GA version, TiDB is
- A freely scalable (computing,storage) database
- Compatible with MySQL syntax and protocol
- Transparent Data Spliting Policy - Range Spliting
- Strongly consistent,distributed transaction support
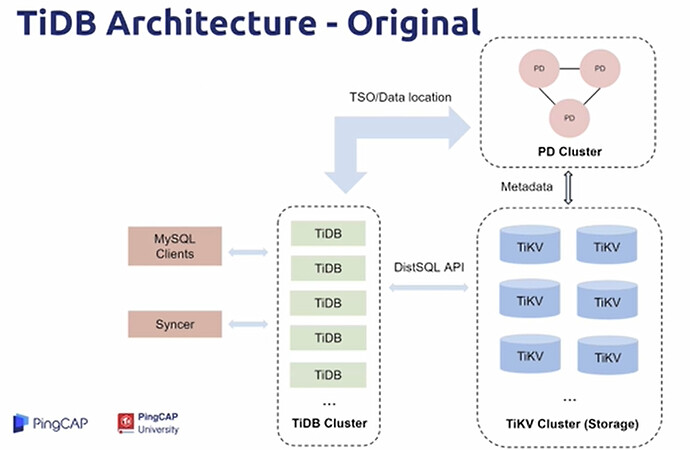
TiDB Architecture - Original
In short: different sizes of the same model
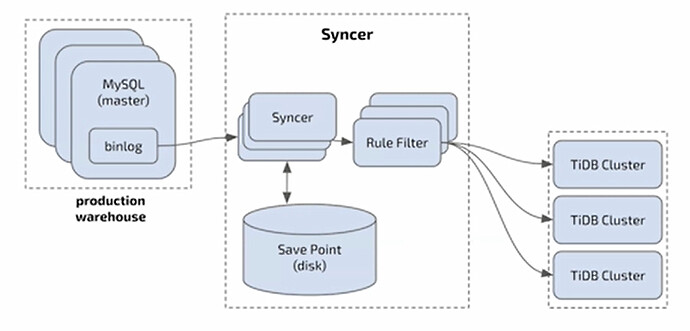
Datahub Capability - Syncer
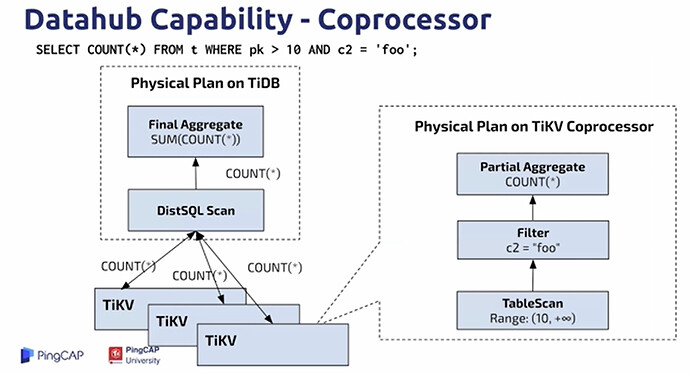
Datahub Capability - Coprocessor
Datahub Capability
- TiDB is ideal for Datahub senarios
- Protocol-compatible, easy synchronization of MySQL production libraries
- Transparent and accessible cross-segmentation queries
- Data landing in real time
- Massive storage allows multiple data sources to converge
- Standby - Datahub Analysis 2-in-1
One year later
- TP Scenario
- CUSTOMER: There are still some problems though… Smells good!
- AP Scenario
- Client 1: Complex statements are so slow!
- Client 2: Always OOM!
- Client 3: Can’t integrate with a big data platfrom!
Choice
- Either combine TiDB or TiKV together
- Complete refactoring of optimizers and actuators to build MPP Engine
- High risk and long duration
- OR,
- The need for an open source distributed computing framework
- High maturity and wide user base
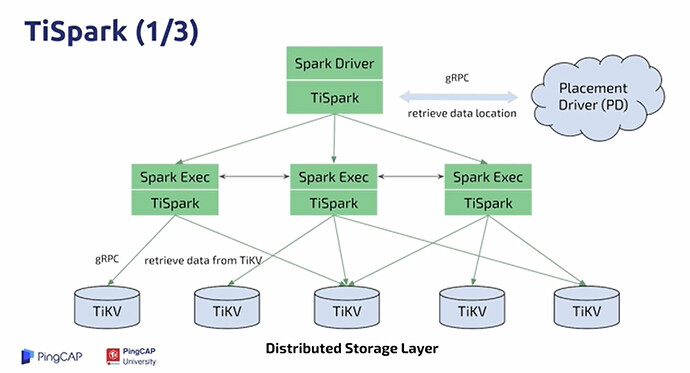
TiSpark (2/3)
- Spark helps us do distributed computing
- A mature distributed computing platform
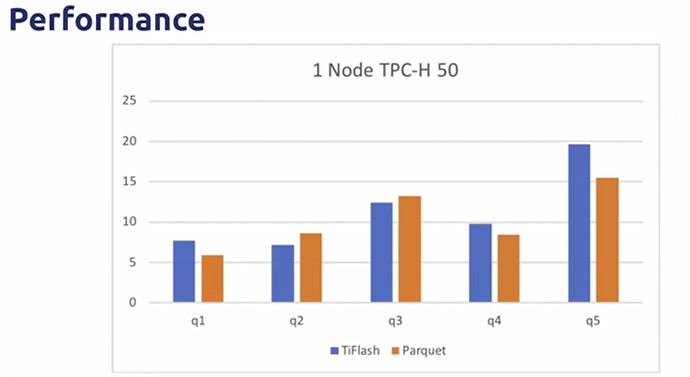
- Faster(?),more stable(?).
- Complete succession to the Apache Spark ecosystem
- Painlessly integrating into the big data ecosystem
- Scripting,Python,R,Apache Zeppelin,Hadoop…
TiSpark (3/3)
- Apache Spark can only provide low concurrency computation
- Heavy computational model and high resource consumption
- Better for Reports and Heavyweight Adhoc Queries
- Users stil need high concurrency,small to medium-sized AP capacity in many situations
- Complex query capability with low consumption
- TiDB is far simpler to maintain than Spart clusters.
Meanwhile…
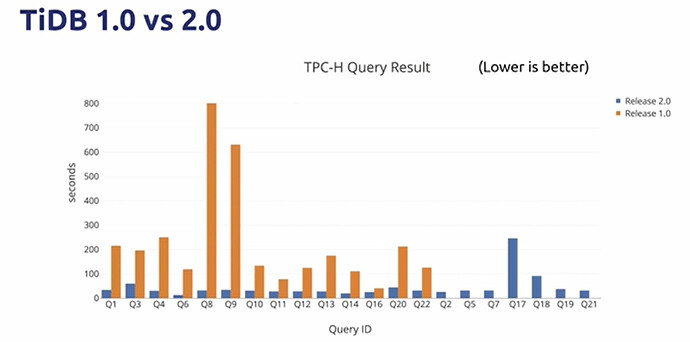
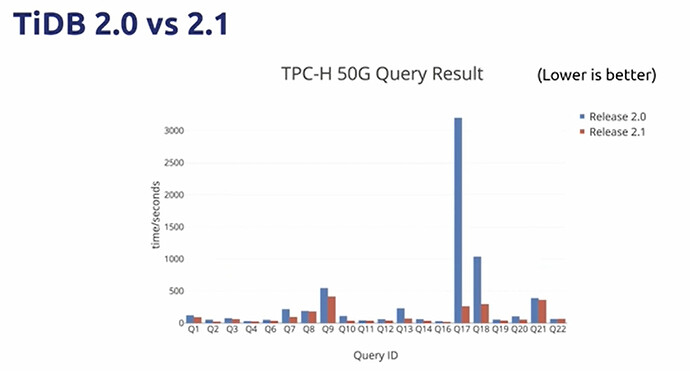
- We were also working on various optimizations around stand-alone TiDB
- Smarter,more efficient and faster in small to medium scale scenarios
- Optimizer
- Basic optimizer? → RBO + CBO Optimizer → Cascades Optimizer (WIP)
- Executor
- Classic Volcano Model → Batch Execution → Vectorized Execution
- Better Concurrency and Pipeline
- Partition tables,Index Merge,etc.
Core conflict
- At this point,we were still left with 2 core contradictions.
- Row storage is not friendly to analysis scenarios
- “How dare you call yourelves HTAP without column store?”
- Workload isolation is not possible
- “I ran a query and the CPU usage was 1000%”
- TiSpark scenarios would be worse.
- Row storage is not friendly to analysis scenarios
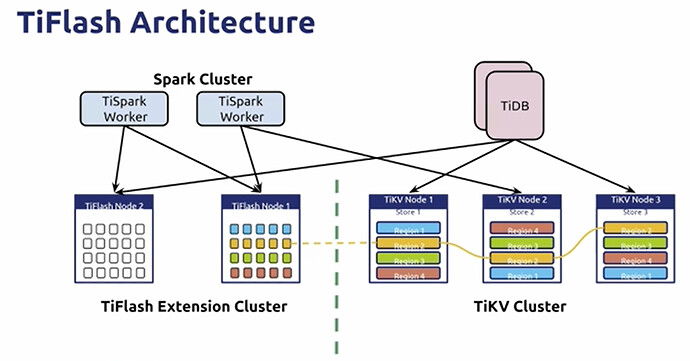
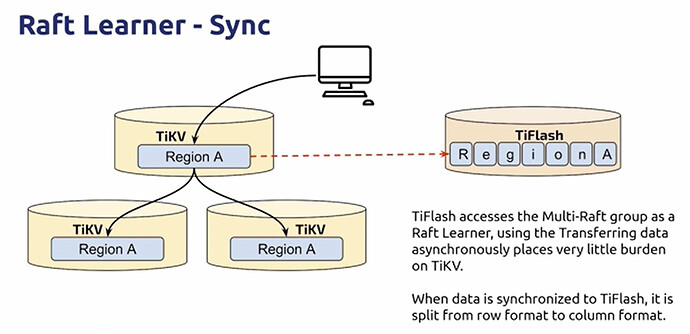
TiFlash
- Synchronize a set of column storage independently via Raft Learner
- Raft Learner provides extremely low consumption copy synchronization
- Raft Learner read protocol works with MVCC to provide strong and consistent reads
- Physical isolation via Label
- AP / TP workloads do not affect each other
Till now
- TiDB =
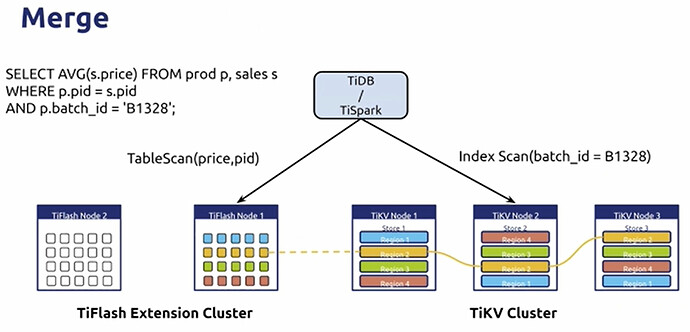
X% TP + Y% AP= HTAP- TiDB doesn’t require you to choose TP or AP,it’s HTAP.
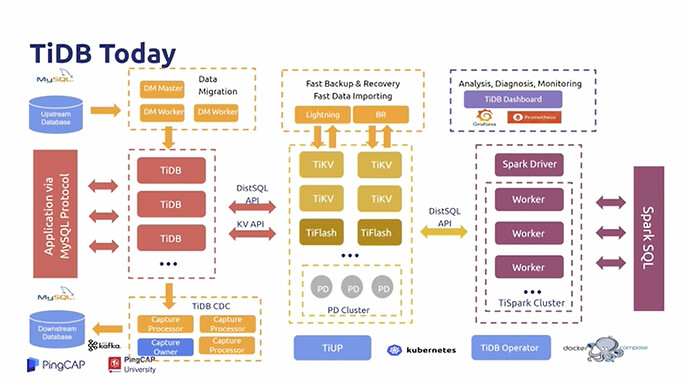
- One Platform,compatible with row and column storage
- Painless data synchronization
- Easy to analyze on columns when the main TiDB cluster runs TP services